Running a website without user data is like embarking on a journey without a compass or GPS. You’re left wandering aimlessly, unsure of which paths to take and which roads lead to your destination – in this case, your online success. Do you know where users click? How do they navigate through your website? Are they able to find the information they need? Understanding these aspects of user behavior is essential to improving the user experience on your website. Enter website tracking, which enables you to track users and gather valuable insights that help you improve your website’s performance. In this article, we will delve into the world of website tracking and explore how it becomes your guiding star on the vast digital landscape. We will also discuss the best practices for tracking users without breaking the law.
What is website tracking?
Website tracking is the process of collecting and analyzing data about how people behave when they visit a website. It’s a crucial tool for any website owner. It allows you to identify everything from the number of visitors that come to your site, where they came from, how long they stay, and how they interact with the site while they’re there. It helps you determine what you’re doing right, what needs improvement, and what needs to change on your site.
There are two kinds of web tracking: first-party and third-party. First-party tracking involves collecting information about website visitors directly on the website itself. This includes data such as IP addresses, page visits, and user behavior. Third-party tracking, on the other hand, occurs when an external site or service tracks user activity across multiple websites. This type of tracking is often used by advertisers and marketers to gather data on user behavior and interests to target ads more effectively.
Skip to “How to track users without breaking the law“
Skip to “How to stop website tracking“
Why do websites track users?
There are more than 5 billion active internet users in the world. The rise of big data and analytics has created a lot of reasons why websites track users. Many websites do it to improve their products, services, performance, usability, and security. Websites can monitor user activity to understand their visitors and the impressions their sites make.
Some of the key reasons for internet tracking include:
- Providing tailored user experiences: Businesses track their website visitors to learn more about their online customers and users. By monitoring how users interact with the site, businesses can gain valuable insight into their customers and how they behave online, which can then be used to tailor user experiences.
- Measuring success: Tracking website visits helps identify successful campaigns and marketing efforts that are driving traffic to your site. By tracking traffic to a site, you can see which types of content are most popular and which pages get the most traffic. For example, Google Analytics lets you track which pages are performing well by tracking their page views, bounce rates, session duration, etc. This information can help businesses focus on the most successful strategies for their websites and stop wasting time on ineffective strategies.
- Delivering targeted advertisements: Targeted advertising enables businesses to display ads that are more relevant to their customers and are therefore more likely to succeed than randomly placed ads. Analytics data help businesses see which types of ads perform best and track the revenue they generate, whether from clicks or purchases. The data also helps businesses ensure that their ads appear in front of the right audience.
- Tracking conversions: It is important to understand where your leads are coming from, especially if you want to attract new customers. By tracking visitors on your site, you can see which efforts are working and which aren’t so you can invest time and budget accordingly.
How do websites track users?
Websites track you in a bunch of different ways, including mouse tracking, eye tracking, click tracking, etc. Let’s look at the most common methods of website tracking:
IP Tracking
An IP address is a unique number that identifies users’ devices online. Although anyone can see their IP address, its location doesn’t tell them anything personal about users. However, by determining where their device is located, a website can determine what country they are in and even what city or region. This is useful for creating targeted campaigns, as well as for security purposes.
Cookies
Cookies are one of the more common ways websites track you. A cookie is a file that a website stores on a user’s computer or mobile device when you visit them. The files contain information about their activities online allowing sites to remember their preferences and personalize their experience when you revisit them. For example, e-commerce sites use cookies to remember users’ shopping carts even after they close the site.
Around 40% of websites on the web use cookies one way or the other.
Learn more about tracking cookies.
Fingerprinting
Fingerprinting is a method of tracking that creates a “fingerprint” of each user’s device, based on information like their operating system, screen size, language settings, IP address, and installed browser plugins. This allows websites to create and store a unique profile for each visitor that comes to their site. Browser fingerprinting is done via JavaScript code that runs in the background of your browser and creates a unique identifier for each user.
Tracking pixels
A tracking pixel or a web beacon is an image file (usually a transparent GIF) that contains a code that can “track” if you have opened an email or visited a website. The code is embedded within the image and is not visible to the user. When the user opens the email or visits the website that contains the pixels, the code executes and tracks their activity. This data can then be used by marketers to analyze visitor behavior and optimize their marketing strategies accordingly.
What is cross-website tracking?
Cross-site tracking is a technical term that refers to the tracking of a user’s activity across multiple websites or domains. It is often used for marketing purposes, to analyze and improve the customer experience, and in some cases, for fraud detection.
Cross-site tracking can be achieved by placing a small piece of code on a site, which is then used to track the activity of users who visit other websites. The main purpose of cross-site tracking is to determine which products or services are of interest to users visiting another website. This allows marketers and webmasters to improve the customer experience on their sites by using data from visits to other sites to deliver targeted advertising and relevant content. This process is referred to as remarketing.
For example, this is how cookies retarget visitors:

Privacy laws on website tracking
GDPR and website tracking
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a set of rules designed to protect people’s personal information. It gives individuals more control over their data and requires website owners to be transparent about how they track users. This has had a big impact on how websites handle user information.
Under the GDPR, websites must clearly explain how they track users and give them the option to say no to being tracked. They can’t use technologies like cookies to monitor user behavior without getting permission first. Websites need to provide a notice to users about their tracking practices and make it easy for users to opt out if they don’t want to be tracked. It’s also important for websites to keep records of users’ consent and explain how they use the data they collect.
CCPA and website tracking
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) are privacy laws in California that regulate how businesses handle personal information. They require businesses to inform consumers about the collection and use of their personal information. Consumers have the right to opt out of the sale of their information and request its deletion. The laws also impact website tracking by requiring businesses to provide clear notices and opt-out mechanisms for tracking technologies and targeted advertising. Compliance involves updating privacy policies and honoring consumer privacy preferences.
How to track website users without violating the law?
All the laws regulating how websites track users do not mean a full stop on track. It means that you should make an extra effort to make it privacy-friendly and put users first.
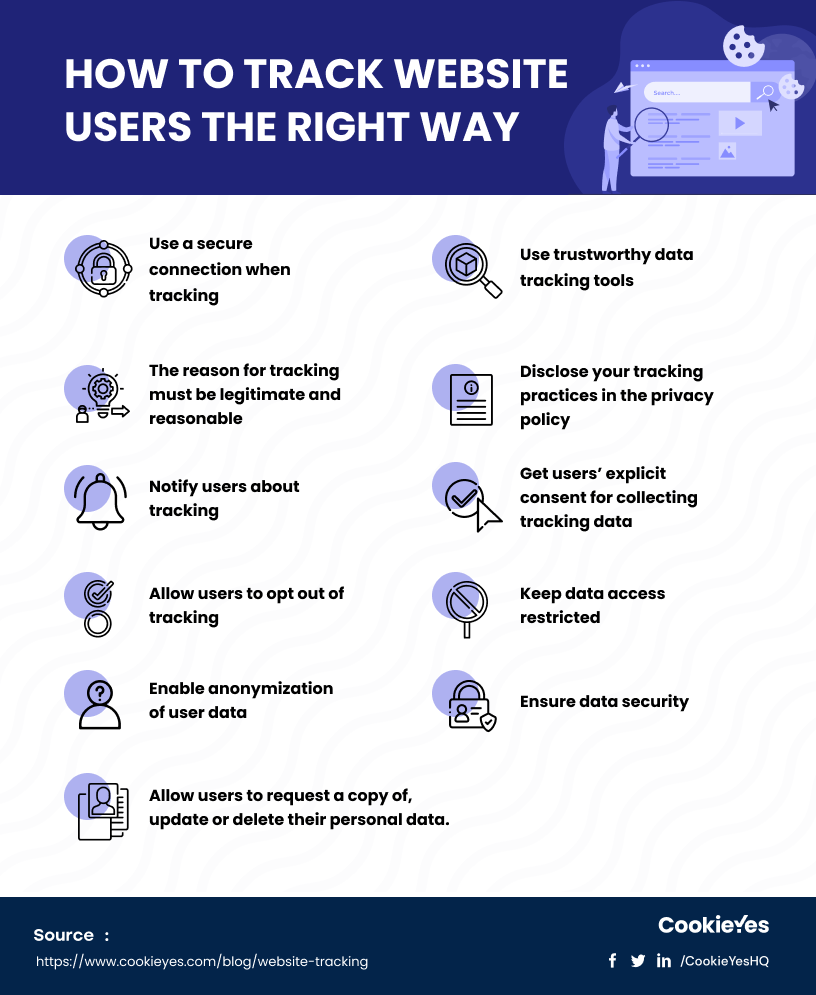
Here are key requirements to follow if you want to track website users legally, without any violation:
- Use a secure connection when tracking, collecting, and transferring data.
- Use trustworthy data tracking tools that are reliable and accurate, yet complies with evolving laws.
- Ensure you have a legitimate and reasonable purpose for tracking.
- Explain your data collection practices in the privacy policy on your website and make it easy for users to find.
- Use a banner or pop-up window to obtain consent from users before collecting any data.
- Ask clear, specific questions when requesting consent
- Avoid pre-checked boxes or checkboxes for asking consent to track users. Users should actively check the box themselves and give their consent.
- Allow users to opt out of tracking by providing an easy way to withdraw consent.
Use tracking cookies
without breaking the law
Hassle-free cookie banner setup and cookie consent management for GDPR and CCPA compliance.
Free Cookie BannerFree 14-day trialCancel anytime
- Keep data access restricted to those with a legitimate need to know, and keep track of who has access.
- Anonymize user data before storing them.
- Ensure the security of data, including protection from external intruders (hackers) and internal misuse (your own employees).
- Allow users to request a copy of their personal data, and ensure the user has the option to update or delete the information you have collected.
Popular tools used for website tracking
Here are some popular website tracking tools used by many websites:
Google Analytics: It is a free, comprehensive web analytics service offered by Google. It tracks and reports on various aspects of website traffic, including page views, session duration, and sources of traffic. In addition, it offers a range of features such as demographic and conversion reports and integration with other Google tools such as AdWords. Google Analytics can be used to analyze various types of websites, including online stores, blogs, and social media platforms.
Hotjar: It is a tool that helps businesses understand how their website is being used using heat maps, visitor recordings, and feedback forms. Heat maps show where users are clicking/taking action on a page, helping you to identify which areas are most popular. Visitor recordings allow you to see exactly what users are doing on their websites, including where they are clicking and how they are interacting with various elements of the page. Feedback forms enable websites to collect feedback directly from users.
Mixpanel: It is a tool that provides real-time tracking and analysis of your product, including the ability to track events, funnel, conversions, engagement, and user profiles on the website or mobile applications.
Clarity: It is a tool from Microsoft that helps businesses understand how users interact with their websites through heat maps and visitor recordings. It offers user testing to see how users interact with websites in real time and gather feedback on their experiences.
Adobe Analytics: It is a web analytics tool that provides detailed insights into website traffic and user behavior. It also integrates with Adobe Experience Platform, which can be used to create personalized experiences for users and perform A/B tests.
How to stop website tracking?
If you are a website user, there are many reasons why you might want to stop website tracking. The most common of these is to reduce the amount of personally identifiable information that websites can gather about you. Whatever your reason for wanting to stop website tracking, there are many ways to do it. Some of them take time and effort on your part, but others require almost no effort at all. Keep in mind not all of them are foolproof methods.
- Limit the information you share online: When using the web, think twice before submitting personally identifiable information.
- Browse in incognito or private mode: Incognito mode is a setting in your browser that allows you to surf the web without leaving a history of your browsing patterns. The website won’t be able to see any data outside of your current browsing session.
- Use anti-tracking tools: Use browser extensions, apps, privacy-friendly browsers, and/or search engines that block trackers. For example, a virtual private network (VPN) hides your IP address as you move through the web, preventing sites from tracking your browsing habits. You can also use settings on your browser that block trackers such as those in Firefox and Safari.
- Clear website data: Clear your browser’s cache, history, or other data that may be tracking your computer use regularly. It’s easy to check cookies on a website.
- Enable browser signals like GPC and DNT: Enable Global Privacy Control (GPC) and Do Not Track (DNT) in your browser to stop website tracking. GPC sends a privacy request header, while DNT indicates your preference not to be tracked. However, website support with these signals varies. Use additional privacy measures for enhanced online privacy.
- Log out of social media when not in use: To prevent Facebook and Twitter from gathering information about your browsing habits on other websites, try staying logged out when you’re not using them.
- Block cookies: You can block all cookies (not recommended) or third-party cookies so they don’t store any information. This can make it harder for websites to track you. However, some websites may break or malfunction.
- Block tracking cookies: Some websites will provide you with a privacy policy that allows you to opt out of tracking cookies.
Frequently asked questions
What is tracking on a website?
Tracking on a website is the act of collecting information about the user’s activity on a website. It can be used to learn more about your users and to make your website better. Tracking can be done either through a third-party service or by directly adding code to your site. For example, Google Analytics records page views, the time spent on each page, bounce rate, and search keywords.
What is web tracking used for?
Web tracking is used for collecting valuable information about website visitors and how they interact with the site. This information is then used to customize the browsing experience for users to increase their level of engagement with the site, and also in the digital economy as a basis for analytics, marketing, and advertising.
Is website tracking illegal?
In theory, website visitor tracking isn’t illegal; it allows websites to deliver better services. However, it has become clear in recent years that users are concerned about their privacy online. In response, many countries have passed legislation to prevent tracking or at least make it clear when it goes on.
Does website tracking affect SEO?
No, website tracking does not directly affect the SEO of your website. Search engines will still crawl your site, regardless of whether or not you have code that tracks user behavior on your pages. You might see an impact on rankings if you implement a third-party analytics tool that slows down your page load times.
Does website tracking affect page load speed?
Yes, it can impact page load times depending on how many scripts are running as well as how these scripts are configured and implemented. Your site may load slowly if you’ve implemented multiple scripts from third-party plugins and services.